Conclusion. #
Summary: Part I #
- Basic Programming Constructs
- for/while
- if/then/else switch/case
- variables, literals, basic datatypes
- basic I/O: printf/scanf
- Pointers, Array, Strings
- pointer arithmetic
- dynamic memory allocation malloc/free
Summary: Part II #
- Recursion
- Abstract Data Types
- Structs, Struct Array, Struct Pointer, Struct of Struct
- Recursive structs using pointers
(Linked Lists, Social Net)
- File I/O : fgets/fputs fscanf/fprintf fread/fwrite
- Misc
- Macros
- Commandline Arguments
- Multifile Programs
- C std Libraries
Programs Covered #
- Store Reciept Management System
- Social Network
- Bank Account Management
- Linked Lists
C Features not covered #
- Unions and Bitfields
- Macros with arguments
Languages/Tools to explore #
- Make files
- Git Version Control
- TMux: Terminal Multiplexer
- C++ Programming
- Object Oriented Programming
- Generic Programing (STL)
- Other Languages
- Python
- Golang
- Haskel
- Swift/Kotlin/C#/Java/Dart
Upcoming Courses #
- Datastructures and Algorithms
- Algorithm Design
- Computer Systems Organization
- OS and Compilers
Recursion and Fractals #
https://fiddle.skia.org/c/7b96d0cb407d99a0e81ed220ba47409c
Homework #
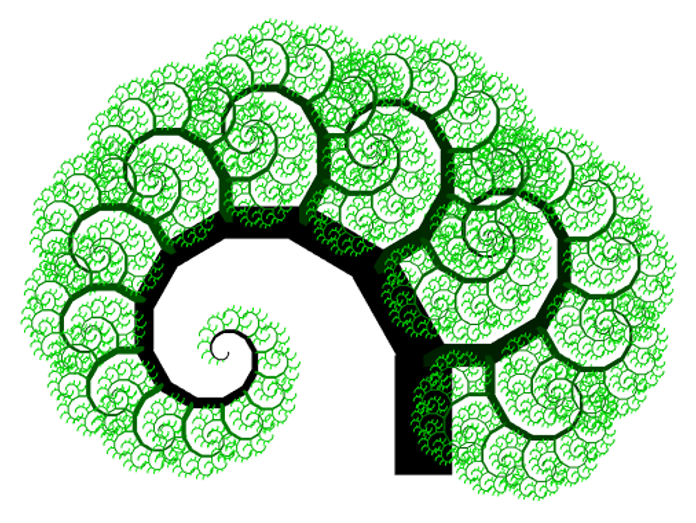


HW: Draw above using https://fiddle.skia.org. See examples of drawing API here 1 2 3.
Recursion in Nature #

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Romanesco_broccoli
Fractals #
https://cpro-iiit.github.io/docs/course_material/projects/practice/#project-9---fractals
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fractal
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mandelbrot_set
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Julia_set
Some Books #
- Godel, Escher & Bach, David Hofstradter.
- Emperors New Mind, Roger Penrose.
Simulations #
Margaret Hamilton #
Appolo Missions (1960) Softare Architect
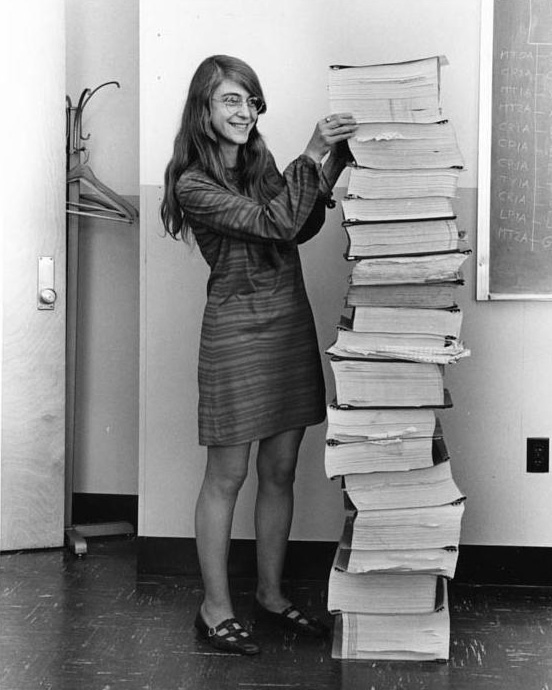 https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/people/320/margaret-hamilton/
https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/people/320/margaret-hamilton/